How does the Budget Speech affect you, your property transactions and your estate?
On 21 February 2018, Finance Minister Malusi Gigaba delivered his 2018 Budget Speech.
Hereby a summary of the most significant proposals for the 2018/2019 Budget as tabled by the Minister of Finance:
2018/2019 Tax Proposals:
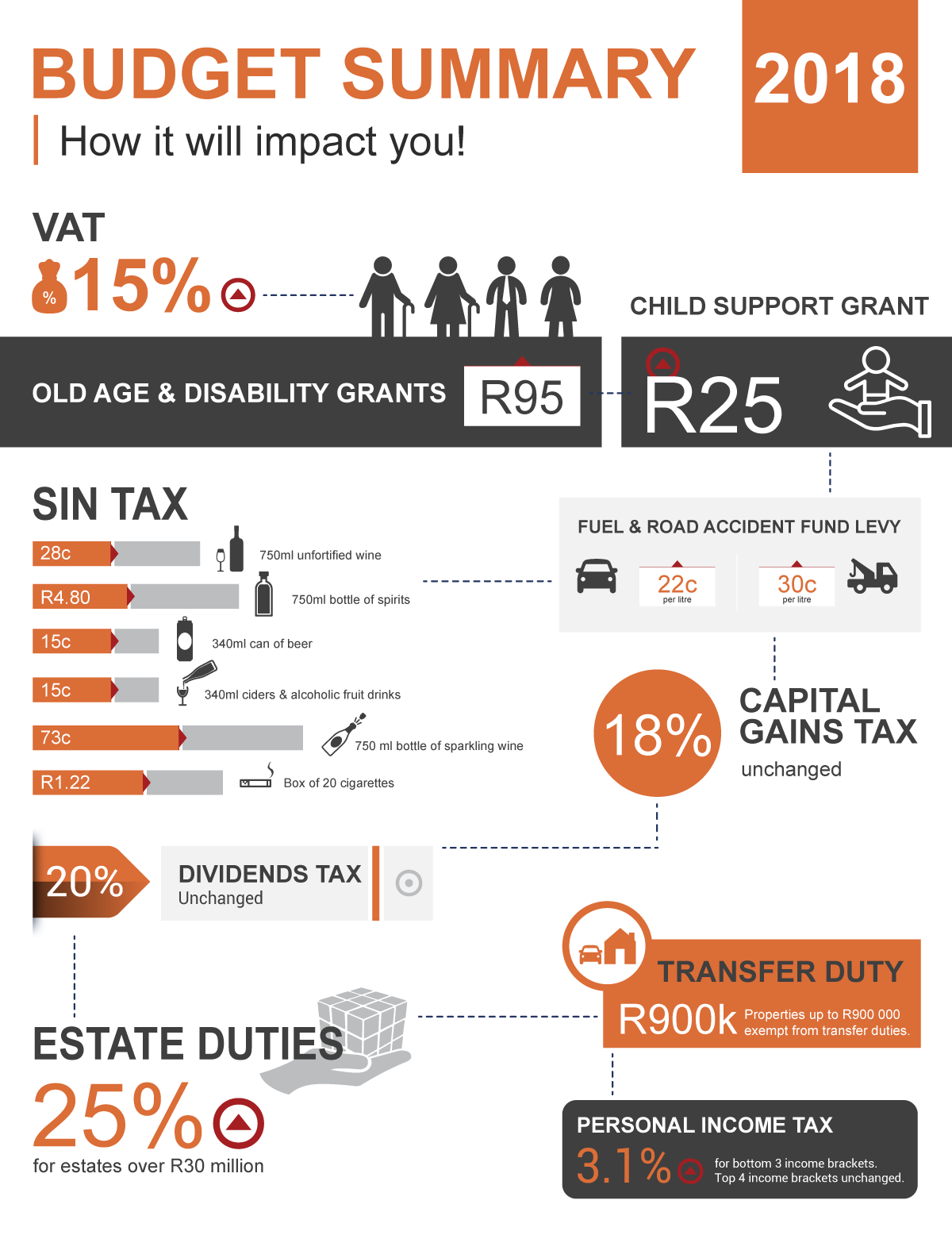
- VAT: A one percentage point (1%) increase in VAT from 14% to 15%.
- No adjustments to the top four income tax brackets. Below inflation adjustments to the bottom three income tax brackets proposed.
- Fuel Levies: Overall increase of 52c/litre for fuel, consisting of a 22c/litre increase in the general fuel levy and 30c/litre increase in the Road Accident Fund levy, effective 4 April 2018.
- Luxury Goods Tax: Increase in the ad-valorem excise duties rate on luxury goods from 7% to 9% effective 1 April 2018.
- Estate Duty Tax: Increased estate duty, to be levied at 25% for estates above R30 million, effective 1 March 2018. This is a 5% increase.
- Capital Gains and Dividend Tax: The capital gains tax rate for individuals remains unchanged at 18%, while the dividends tax rate remains unchanged at 20%.
- Medical Tax Credits: The medical tax credits will increase from R303 to R310 per month for the first two beneficiaries (2.3% increase), and from R204 to R209 per month for the remaining beneficiaries (2.5% increase).
- Sin Tax: Excise duties on tobacco products will increase by 8.5% and on alcohol by 6-10%.
- Environmental & Health Tax: Increases in the plastic bag levy, the motor vehicle emissions tax and the levy on incandescent light bulbs to promote eco-friendly choices.
Transfer Duty Fees:
Transfer duty fees have remained unchanged. The following rates on transactions in respect of acquisition of property is payable (and not subject to VAT).
| Value of Property (R) | Rate |
| 0 – 900 000 | 0% |
| 900 001 – 1 250 000 | 3% of the value above 900 000 |
| 1 250 001 – 1 750 000 | 10 500 + 6% of the value above 1 250 000 |
| 1 750 001 – 2 250 000 | 40 500 + 8% of the value above 1 750 000 |
| 2 250 001 – 10 000 000 | 80 500 + 11% of the value above 2 250 000 |
| 10 000 001 and above | 933 000 + 13% of the value above 10 000 000 |
Estate Duty Tax:
The 2018 Budget proposes to increase estate duty from 20% to 25% for estates worth R30 million and more. This is in line with Davis Tax Committee recommendations, and in keeping with the progressive structure of the tax system. Any donations above R30 million in one tax year will be taxed at 25%, in order to limit the staggering of donations and avoid the higher estate duty rate. Both measures will be effective from 1 March 2018.
Estate duty is levied on property of residents and South African property of non-residents less allowable deductions. The duty is levied on the dutiable value of an estate at a rate of 20% on the first R30 million and at a rate of 25% above R30 million. A basic deduction of R3.5 million is allowed in the determination of an estate’s liability for estate duty as well as deductions for liabilities, bequests to public benefit organisations and property accruing to surviving spouses.
- SAICA 2018 Budget Tax Commentary and Summary – Download here
- SARS Budget 2018 Tax Guide – Download here